Discover How DMart is Changing the Game: A Retail Revolution Success Story
Business Case Study Series
DMart: A Comprehensive Business Case Study
1. Introduction
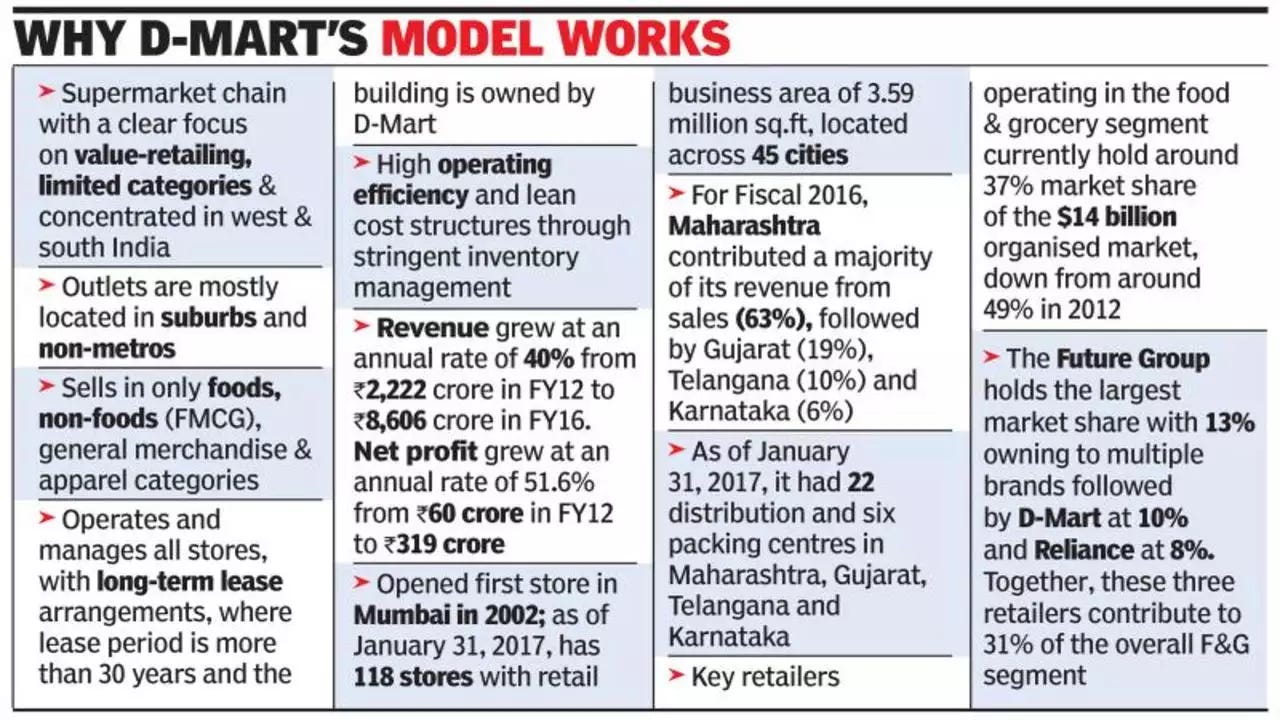
DMart, an Indian supermarket chain founded in 2000, has quickly become one of the most successful retail chains in India. Known for its low-price strategy and customer-first approach, DMart has revolutionized retail by focusing on cost efficiency and product assortment. This case study explores DMart’s business model, growth strategies, challenges, and adaptation to changing market dynamics, offering insights for Home School of Business students.
2. Company Overview
Founder: Radhakishan Damani
Founded: 2000
Headquarters: Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Industry: Retail (Supermarket/Hypermarket)
Core Products: Groceries, FMCG products, apparel, kitchenware, home appliances, and general merchandise
Global Presence: Primarily focused on India, with over 300 stores across the country
Parent Company: Avenue Supermarts Ltd.
3. Market Analysis
Market Size: The Indian retail market is expected to reach $1.8 trillion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 10%. DMart holds a significant market share in the organized retail sector, particularly in groceries and FMCG.
Consumer Behavior: With an increasing preference for value-based shopping, customers seek low-cost, high-quality products. DMart’s target market includes middle-class families and value-conscious customers who prioritize affordability over brand exclusivity.
Key Competitors: Reliance Retail, Big Bazaar, Spencer’s, More, and e-commerce players like Amazon and Flipkart.
4. Business Model
DMart operates a low-cost, high-volume business model, emphasizing efficient store operations and product offerings to maximize profitability. It has adopted an everyday low-price (EDLP) strategy, appealing to price-sensitive consumers.
Key Elements:
Product Range: DMart’s product portfolio includes groceries, home essentials, personal care products, and general merchandise. It primarily focuses on high-turnover categories like food, toiletries, and FMCG.
Store Format: DMart operates large-format stores (supermarkets and hypermarkets) in high-traffic locations, strategically located in densely populated areas to capture maximum footfall.
Revenue Streams:
In-store Sales: DMart’s primary revenue comes from its brick-and-mortar stores, offering a variety of essential goods.
Private Labels: The company has launched private label products that offer higher margins and control over product quality.
Online Sales: Through DMart Ready, the company is exploring e-commerce to reach digital-savvy customers.
Cost Efficiency: DMart focuses on lean operations, including owning store properties, centralized procurement, and maintaining a minimal advertising budget to keep costs low.
5. Evolution and Growth
Founding and Early Success: Radhakishan Damani, a stock market investor, founded DMart in 2000 with a single store in Mumbai. His vision was to create a retail chain that provided everyday low prices on essential products.
Expansion: DMart gradually expanded across Maharashtra and other key states, focusing on owning the properties where it operates stores to minimize rental expenses and maintain cost control.
IPO and Public Listing: In 2017, Avenue Supermarts Ltd., DMart’s parent company, went public with a highly successful IPO, marking a major milestone in its growth trajectory. The company’s shares have consistently outperformed the broader market.
Online Presence: In response to the growing demand for online shopping, DMart launched DMart Ready, a grocery delivery and pick-up service, catering to urban consumers.
6. Operational Strategy
DMart’s operational strategy focuses on cost efficiency, optimizing supply chain management, and strategic real estate investments.
Key Aspects:
Ownership of Store Properties: By owning most of its store properties, DMart avoids paying high rentals, which significantly reduces operating costs and ensures long-term stability.
Inventory Management: DMart maintains tight control over inventory, ensuring that high-demand products are always in stock, reducing holding costs and increasing turnover.
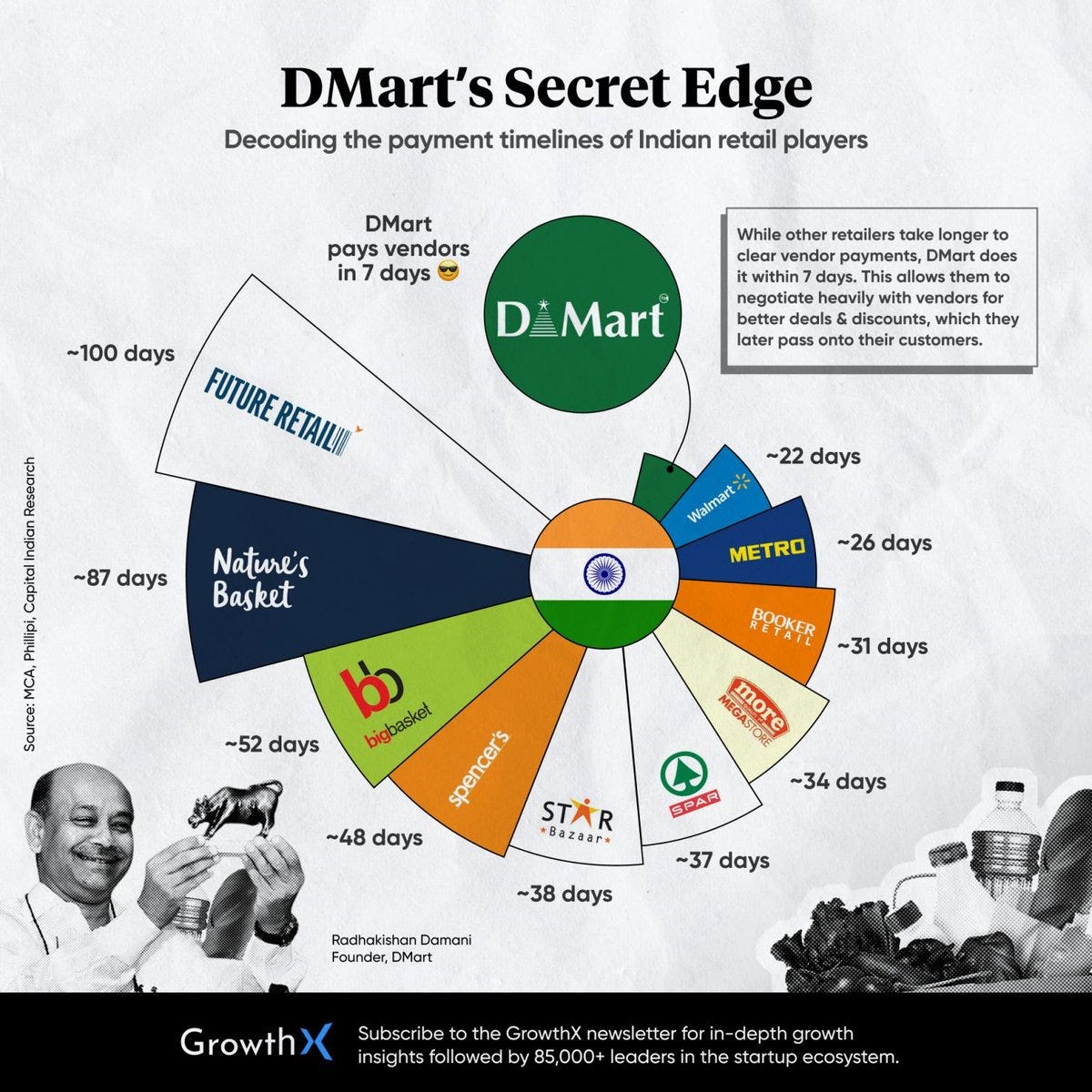
Supply Chain Efficiency: The company operates a centralized procurement system, negotiating directly with suppliers to get the best prices. This strategy allows DMart to pass on cost savings to consumers.
Customer-Centric Approach: DMart prioritizes offering quality products at lower prices, enhancing customer loyalty and ensuring high foot traffic.
7. Financial Analysis
DMart’s financial performance has been consistently strong, driven by efficient operations and a high customer retention rate.
Revenue: DMart reported annual revenue of ₹31,000 crore ($4 billion) in FY2023, with significant contributions from groceries and FMCG products.
Costs: Major costs include procurement of goods, operational expenses (staffing, store maintenance), and logistics. Owning stores helps mitigate rental costs.
Profitability: Due to its efficient cost structure, DMart consistently delivers strong profit margins, outperforming many competitors in the organized retail sector.
Cash Flow: DMart’s focus on high inventory turnover and low operating costs has resulted in strong cash flow generation, which the company reinvests into expanding its store network.
8. Marketing and Customer Acquisition
DMart’s marketing approach is minimal, relying on word-of-mouth and its EDLP strategy rather than expensive advertising campaigns.
Target Market: DMart targets middle-income families and price-sensitive customers, offering them value for money through everyday low prices on essential goods.
Marketing Channels: Unlike its competitors, DMart does not invest heavily in traditional advertising or promotions. Instead, it relies on its pricing strategy and customer loyalty to drive foot traffic.
Customer Engagement: DMart uses a simple, no-frills store layout, focusing on delivering a consistent shopping experience. Customers trust DMart for its competitive pricing and product availability.
Online Strategy: Through DMart Ready, the company has ventured into e-commerce, offering customers a digital platform for grocery shopping with a convenient pick-up or delivery option.
9. Challenges
E-commerce Competition: With the rise of online grocery platforms like BigBasket, Amazon, and Flipkart, DMart faces increasing competition in the e-commerce space, especially from tech-enabled players offering rapid delivery.
Limited Presence in Non-Metro Areas: While DMart has a strong presence in urban and metro areas, it has yet to penetrate many rural or semi-urban markets, which present significant growth opportunities.
Rising Real Estate Costs: Although DMart owns many of its stores, the cost of acquiring new properties in prime locations continues to rise, posing a challenge for future expansion.
Supply Chain and Inventory Management: Efficiently managing supply chains during crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, remains a challenge. Disruptions in the supply chain can impact inventory availability and customer satisfaction.
10. COVID-19 Impact
Demand Surge: During the COVID-19 lockdowns, DMart saw a surge in demand for essential goods, especially groceries. However, store closures and capacity restrictions affected overall sales.
Accelerated E-Commerce Expansion: The pandemic accelerated DMart’s focus on online grocery services through DMart Ready, as more consumers shifted to online shopping for safety and convenience.
Operational Challenges: The pandemic caused temporary disruptions in the supply chain and workforce management, but DMart adapted quickly by focusing on essential goods and ensuring customer safety in its stores.
11. Future Prospects
Expansion into New Markets: DMart is expected to expand into more Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, capitalizing on the growing demand for organized retail in smaller towns.
Growth of DMart Ready: The online grocery market in India is expected to grow significantly, and DMart Ready is positioned to capture a larger share of this market through its hybrid online-offline approach.
Focus on Private Labels: DMart will likely increase its focus on private label products to improve margins and offer customers a wider range of affordable options.
Sustainability Initiatives: As the retail industry evolves, DMart may need to adopt more sustainable practices, particularly in packaging and supply chain management.
12. SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Strong brand equity and customer loyalty.
Cost-efficient business model with low operational expenses.
High profit margins due to property ownership and supply chain efficiencies.
Weaknesses:
Limited online presence compared to competitors like Amazon and Flipkart.
Slow expansion into non-metro markets.
Opportunities:
Expansion into rural and semi-urban markets.
Increasing demand for online grocery services.
Growth potential in private label products.
Threats:
Intense competition from both traditional and online retail players.
Rising real estate costs and potential supply chain disruptions.
Regulatory changes that could impact the retail industry.
13. Strategic Recommendations
Strengthen E-commerce Presence: DMart should focus on expanding its DMart Ready platform to meet the growing demand for online grocery shopping. By offering more competitive delivery options, it can better compete with online giants.
Rural Market Expansion: DMart should explore store openings in rural and semi-urban areas, where there is an unmet demand for organized retail, particularly for essential goods.
Focus on Sustainability: DMart should invest in sustainable packaging, energy-efficient store operations, and reducing its carbon footprint to align with global sustainability trends.
Enhance Private Label Offering: By expanding its private label range, DMart can offer more affordable alternatives to branded products, improving margins and customer retention.
14. Conclusion
DMart’s success story lies in its ability to combine cost-efficiency with customer-centricity, offering everyday low prices on essential goods. The company’s long-term focus on owning store properties and optimizing supply chain management has enabled it to maintain healthy profit margins while expanding rapidly across India.
With a strong foundation in place, DMart is well-positioned to continue its growth trajectory by expanding into new markets, enhancing its digital presence, and adapting to evolving consumer preferences.
HSB Important Articles and References :Share your feedback and tell us which case studies you'd like to see next by filling out this quick Google form! Click Here
Check and follow up:
1) WhatsApp Channel : Click Here
2) Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/homeschoolofbusiness.in/
DMart (Wikipedia) : Click Here
The Business Model : Click Here
Avenue Supermarkets Stock Analysis : Click Here
DMart Investor Relations and Financials : Click Here
Why DMart shares plunged 9% in early trade today : Click Here
Get to know about Radhakishan Damani : Click Here
DMart Website : Click Here
HSB Video Vault :-
What The Home School of Business Offers:
Business News Letters We Offer:
Business Case Study Series, Scam Series, Leadership Series, Industry Series, City Series, 5 Minute reads.Startup Tips Guide Series: Get step-by-step guidance from idea inception to IPO.
Your journey from an idea to IPO starts here!
Visit our website for all Posts: CLICK HERE
Best Regards,
The Home School of Business Team