Inside Apple Music: How Apple's Streaming Giant Dominates the Global Music Scene
Business Case Study Series
Apple Music: A Comprehensive Business Case Study
1. Introduction
Apple Music, launched in 2015, is a streaming service from tech giant Apple Inc. that provides subscribers with access to millions of songs, exclusive content, and curated playlists. As one of the major players in the music streaming industry, Apple Music has evolved to become a crucial part of Apple’s ecosystem. This case study explores Apple Music’s business model, growth strategies, challenges, and how it has adapted to the evolving digital music landscape, offering insights for Home School of Business students.
2. Company Overview
Parent Company: Apple Inc.
Founded: June 2015
Headquarters: Cupertino, California, United States
Industry: Music Streaming
Core Offerings: Music streaming, curated playlists, podcasts, radio stations, and exclusive artist content
Global Presence: Available in over 160 countries with millions of active users
3. Market Analysis
Market Size: The global music streaming market was valued at approximately $29.4 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach $103 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 14.7%. Apple Music is one of the key players in this highly competitive space, alongside Spotify, Amazon Music, and YouTube Music.
Consumer Behavior: The consumption of music has shifted dramatically toward streaming services, with users valuing access over ownership. Personalization, curated playlists, and exclusive content have become major drivers for user engagement.
Key Competitors: Spotify, Amazon Music, YouTube Music, Tidal, and Deezer.
4. Business Model
Apple Music operates on a subscription-based model, generating revenue primarily from individual, family, and student plans. It offers both an ad-free experience and exclusive content to its users. Apple Music’s integration with Apple’s ecosystem, including iPhones, iPads, and Macs, gives it a competitive edge in user experience and seamless device synchronization.
Product Range:
Music Streaming: Access to over 100 million songs.
Apple Music Radio: Live global radio stations, including Apple Music 1, featuring curated music and artist interviews.
Podcasts: Apple Music provides access to exclusive music-related podcasts and shows.
Music Videos and Exclusives: The platform features exclusive music videos, albums, and content from artists like Taylor Swift, Drake, and Billie Eilish.
Revenue Streams:
Subscriptions: Apple Music offers a tiered subscription model (individual, family, student) that drives the majority of its revenue.
Bundle Deals: Apple Music is also part of the Apple One bundle, which includes other services like Apple TV+, iCloud storage, and Apple Arcade.
Artist Collaborations: Apple partners with artists for exclusive releases and curated playlists, further boosting its revenue.
5. Evolution and Growth
Early Beginnings: Apple Music was launched in 2015, years after competitors like Spotify, but it quickly gained traction due to Apple’s massive ecosystem. The platform built on Apple’s existing iTunes model, transitioning users from music ownership to subscription-based streaming.
Expansion: Over the years, Apple Music has expanded its library, introduced personalized recommendations, and integrated with other Apple services. In 2021, Apple Music introduced spatial audio and lossless streaming, aiming to enhance the audio experience for its users.
Artist Partnerships: Apple Music has consistently worked with top artists and labels to secure exclusive album releases and content, helping differentiate itself from competitors.
6. Operational Strategy
Seamless Integration with Apple Ecosystem: One of Apple Music’s biggest strengths is its deep integration with Apple devices, including iPhones, iPads, Macs, and Apple Watches. This seamless user experience helps drive subscriptions and reduce churn.
Exclusive Content: Apple Music focuses on securing exclusive deals with artists for early album releases, live performances, and behind-the-scenes content. This strategy has helped attract a loyal user base and differentiate itself from competitors like Spotify.
Innovative Features: With spatial audio, lossless streaming, and personalized playlists, Apple Music consistently adds new features to enhance the user experience. Its integration with Siri, Apple’s voice assistant, also makes music discovery and playback more convenient for Apple device users.
Sustainability Initiatives: Apple Music aligns with Apple’s sustainability initiatives, as Apple is committed to making its entire business carbon-neutral by 2030. Apple Music leverages Apple’s data centers, which are powered by renewable energy.
7. Financial Analysis
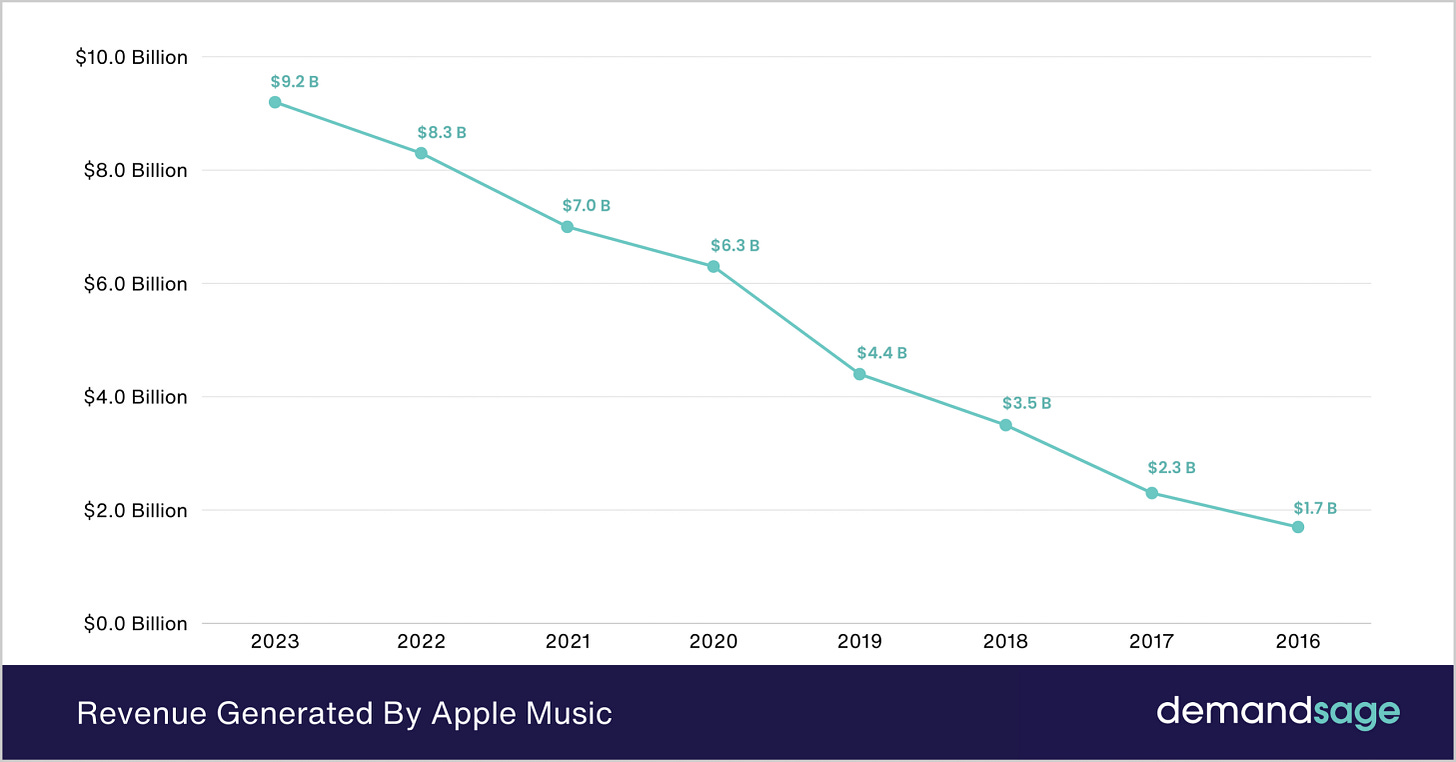
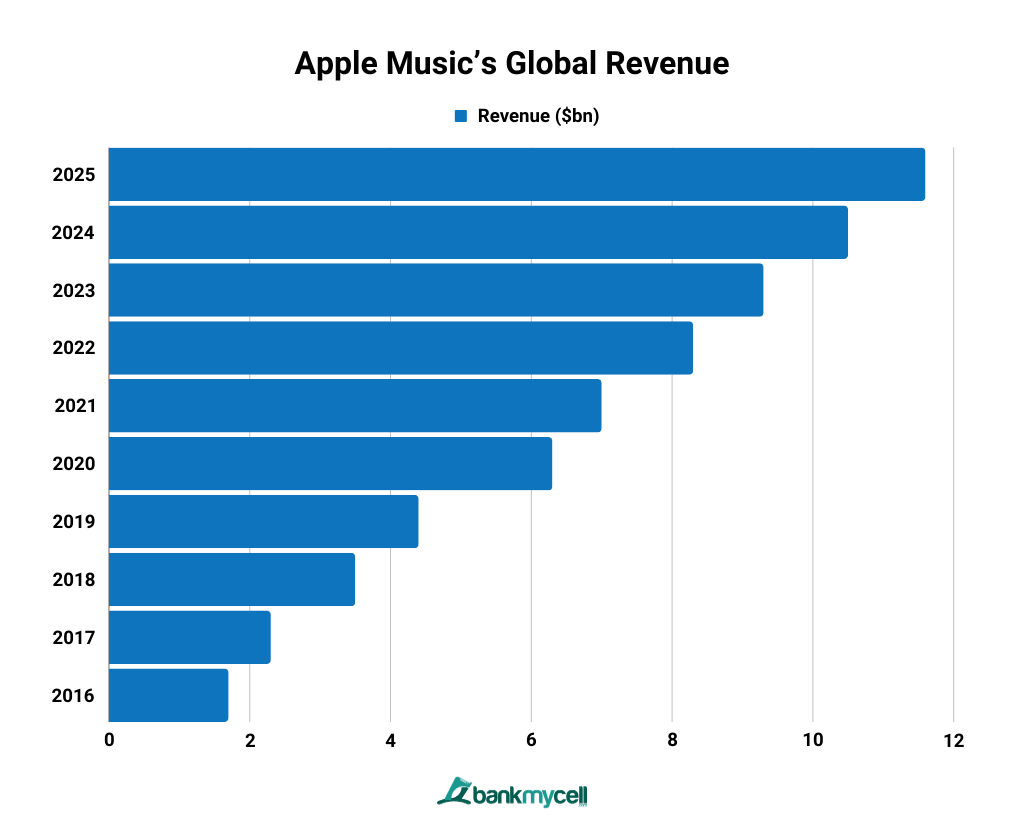
Revenue: Apple Music contributes significantly to Apple’s Services revenue, which was approximately $78 billion in 2022. The service benefits from Apple’s large installed base of over 1.5 billion active devices, providing a ready market for its subscription services.
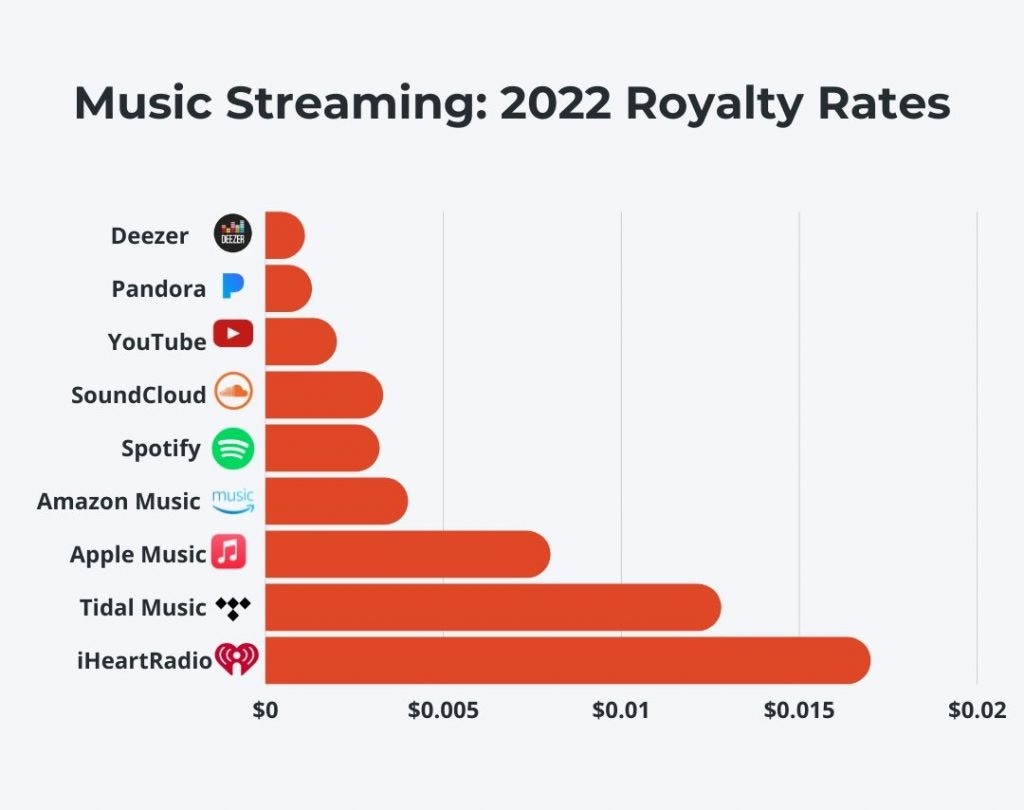
Costs: Apple Music incurs high costs related to licensing agreements with record labels, artist royalties, and platform development. Exclusive content deals and investments in high-quality streaming infrastructure also contribute to its operational costs.
Profitability: While Apple does not break down the specific profitability of Apple Music, the service benefits from Apple’s larger ecosystem and ability to cross-sell other services (like iCloud and Apple One). However, due to the high costs of artist royalties and streaming infrastructure, profit margins can be tighter than in other Apple segments.
8. Marketing and Customer Acquisition
Target Market: Apple Music targets a global audience, with offerings for music enthusiasts, casual listeners, and audiophiles. It caters to individuals, families, and students through its tiered subscription plans.
Marketing Channels:
Apple Ecosystem: Apple Music benefits from being pre-installed on Apple devices, giving it direct access to millions of potential users.
Exclusive Artist Collaborations: Apple Music markets exclusive content from major artists to attract new subscribers and engage existing users.
Digital Marketing and Social Media: Apple Music uses social media campaigns, influencer marketing, and digital ads to target potential users, especially younger audiences.
Customer Engagement: Apple Music focuses on personalization, offering curated playlists like “For You” based on user preferences. Additionally, Apple Music leverages celebrity-curated playlists and live radio shows to keep users engaged.
9. Challenges
Fierce Competition: Apple Music faces stiff competition from Spotify, which leads the global music streaming market, as well as other players like Amazon Music, YouTube Music, and Tidal.
Artist Royalty Disputes: Like other streaming services, Apple Music faces ongoing challenges with artists and record labels over royalty payments, which can impact profitability and public perception.
Customer Retention: While Apple Music benefits from Apple’s ecosystem, it faces challenges in retaining users who have access to cheaper or ad-supported alternatives, such as Spotify.
Market Saturation: The music streaming market is becoming increasingly saturated, and future growth may rely on differentiating through exclusive content, enhanced user experience, or bundled services.
10. COVID-19 Impact
Increased Streaming Demand: The pandemic led to an increase in music streaming as more people stayed home. Apple Music saw a surge in usage as consumers sought entertainment during lockdowns.
Shift in Content Strategy: With live concerts on hold, Apple Music focused on exclusive live-streamed performances and curated content, allowing artists to engage with their fans in new ways.
Adaptation to Remote Work and Study: The rise of remote work and study during the pandemic saw increased consumption of focus and relaxation playlists, providing an opportunity for Apple Music to offer more genre-specific content.
11. Future Prospects
Spatial Audio and Lossless Streaming: Apple Music’s investment in lossless and spatial audio is likely to be a key driver of differentiation. Audiophiles and tech enthusiasts are expected to gravitate toward the service as sound quality becomes a more important factor in music consumption.
Global Expansion: Apple Music is expected to continue growing its subscriber base in emerging markets where digital streaming is on the rise. India, Brazil, and Southeast Asia present significant growth opportunities.
Further Integration with Apple One: Bundling Apple Music with other Apple services through Apple One is likely to increase user retention and drive growth in the Apple ecosystem.
12. SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Strong integration with Apple’s ecosystem.
Exclusive content and partnerships with top artists.
High-quality streaming features (lossless and spatial audio).
Weaknesses:
High dependency on artist royalties and licensing agreements.
Premium pricing compared to ad-supported services.
Opportunities:
Expansion into emerging markets.
Further investment in exclusive artist content and live events.
Continued growth through Apple One bundle subscriptions.
Threats:
Intense competition from Spotify, Amazon Music, and YouTube Music.
Legal and regulatory challenges around royalty payments.
Market saturation in key regions such as North America and Europe.
13. Strategic Recommendations
Focus on Emerging Markets: Apple Music should expand its presence in high-growth regions like India, Brazil, and Southeast Asia, offering localized content and competitive pricing to drive adoption.
Invest in Exclusive Content: Apple Music should continue to secure exclusive artist releases and live performances to differentiate itself from competitors.
Enhance Personalization Features: Continued investment in AI-driven personalized playlists and music recommendations will help Apple Music deepen customer engagement and improve retention.
Expand Spatial Audio Offering: Promoting its superior sound quality with spatial audio will attract audiophiles and consumers who value a premium listening experience.
14. Conclusion
Apple Music has successfully established itself as one of the leading music streaming services in a highly competitive market. By leveraging Apple’s ecosystem, focusing on exclusive content, and enhancing its streaming quality, Apple Music has positioned itself as a premium music service. However, it must continue to address challenges such as competition and artist royalty concerns while exploring growth opportunities in emerging markets and evolving its product offerings to remain a dominant force in the industry.
HSB Important Articles and References :Share your feedback and tell us which case studies you'd like to see next by filling out this quick Google form! Click Here
Check and follow up:
1) WhatsApp Channel : Click Here
2) Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/homeschoolofbusiness.in/
Apple Music (Wikipedia) : Click Here
Apple Music Official Website : Click Here
Revenue and Usage Statistics : Click Here
Apple Music Royalties to the Artists : Click Here
Apple Music vs Spotify : Click Here
HSB Video Vault :-
What The Home School of Business Offers:
Business News Letters We Offer:
Business Case Study Series, Scam Series, Leadership Series, Industry Series, City Series, 5 Minute reads.Startup Tips Guide Series: Get step-by-step guidance from idea inception to IPO.
Your journey from an idea to IPO starts here!
Visit our website for all Posts: CLICK HERE
Best Regards,
The Home School of Business Team