Inside Deutsche Bank’s Global Strategy: Restructuring, Digital Transformation, and Sustainability for Future Growth
Business Case Study Series
Deutsche Bank: A Comprehensive Business Case Study
1. Introduction
Deutsche Bank AG is one of the world’s largest financial services providers, with a global presence in investment banking, corporate banking, private banking, and asset management. Founded in 1870 in Berlin, Deutsche Bank has grown to become a key player in the global banking sector. This case study explores Deutsche Bank’s business model, growth strategies, challenges, and its adaptation to changing financial market dynamics, offering insights for Home School of Business students.
2. Company Overview
Founder: Adelbert Delbrück and Ludwig Bamberger
Founded: 1870
Headquarters: Frankfurt, Germany
Industry: Financial Services
Core Services: Investment banking, corporate banking, private banking, asset management, retail banking
Global Presence: Over 70 countries, with major operations in Europe, the Americas, and the Asia-Pacific region
3. Market Analysis
Global Banking Market Size: The global banking market is projected to reach approximately $12.2 trillion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 4.5%. Deutsche Bank has a notable share in investment banking, private wealth management, and corporate banking.
Market Trends: Key trends shaping the banking sector include digital transformation, regulatory compliance, sustainability in finance, and the rise of fintech.
Key Competitors: JPMorgan Chase, Citigroup, Goldman Sachs, UBS, Barclays, Credit Suisse, and HSBC.
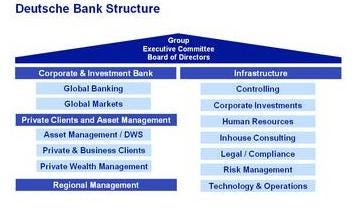
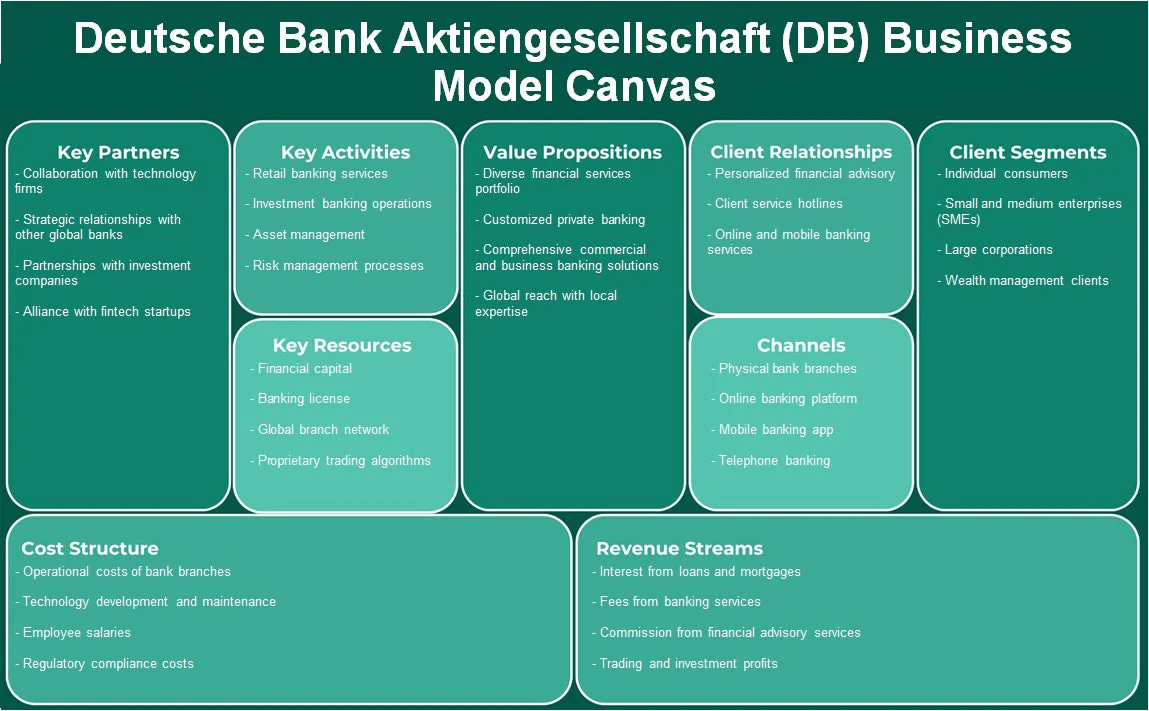
4. Business Model
Deutsche Bank operates a diversified business model, offering a broad range of financial services to corporations, governments, institutions, and individuals globally. It is structured into four core divisions:
Investment Banking: Focuses on capital markets, advisory services, mergers and acquisitions (M&A), and trading of securities and derivatives.
Corporate Banking: Provides transaction banking services, including cash management, trade finance, lending, and treasury solutions.
Private Banking and Wealth Management: Offers tailored wealth management and banking solutions to high-net-worth individuals and family offices.
Asset Management (DWS Group): Focuses on investment products such as mutual funds, ETFs, and alternative investments, catering to both retail and institutional clients.
Revenue Streams:
Investment Banking Fees: A significant portion of Deutsche Bank’s revenue comes from advisory fees for M&A, capital raising, and underwriting.
Interest Income: The bank earns interest income from loans and credit facilities provided to corporate and retail clients.
Asset Management Fees: Revenue from managing investment funds and wealth portfolios.
Trading and Sales: Profits generated from trading securities, foreign exchange, commodities, and derivatives.
5. Evolution and Growth
Early Beginnings: Founded to promote trade between Germany and international markets, Deutsche Bank quickly expanded into global operations.
Post-War Expansion: After WWII, the bank re-established itself as a major international player, particularly in corporate finance and investment banking.
Growth Through Acquisitions: The acquisition of Bankers Trust in 1999 solidified Deutsche Bank’s position in investment banking, particularly in the U.S. markets.
Global Financial Crisis (2008): Deutsche Bank was heavily impacted by the 2008 financial crisis due to its exposure to mortgage-backed securities. The bank had to restructure its operations and refocus on core strengths in the aftermath.
6. Operational Strategy
Global Reach: Deutsche Bank operates through a global network, with a focus on key financial hubs such as Frankfurt, London, New York, and Singapore.
Focus on Digital Transformation: As part of its restructuring efforts, Deutsche Bank has been investing heavily in technology and digital platforms to enhance its client offerings, improve operational efficiency, and stay competitive with fintech firms.
Sustainability in Finance: The bank is committed to promoting sustainable finance by providing green loans, sustainability-linked bonds, and ESG-focused investment solutions.
Cost Reduction Initiatives: To recover from past financial difficulties, Deutsche Bank has implemented a series of cost-cutting measures, including layoffs, divestitures of non-core assets, and office consolidations.
7. Financial Analysis
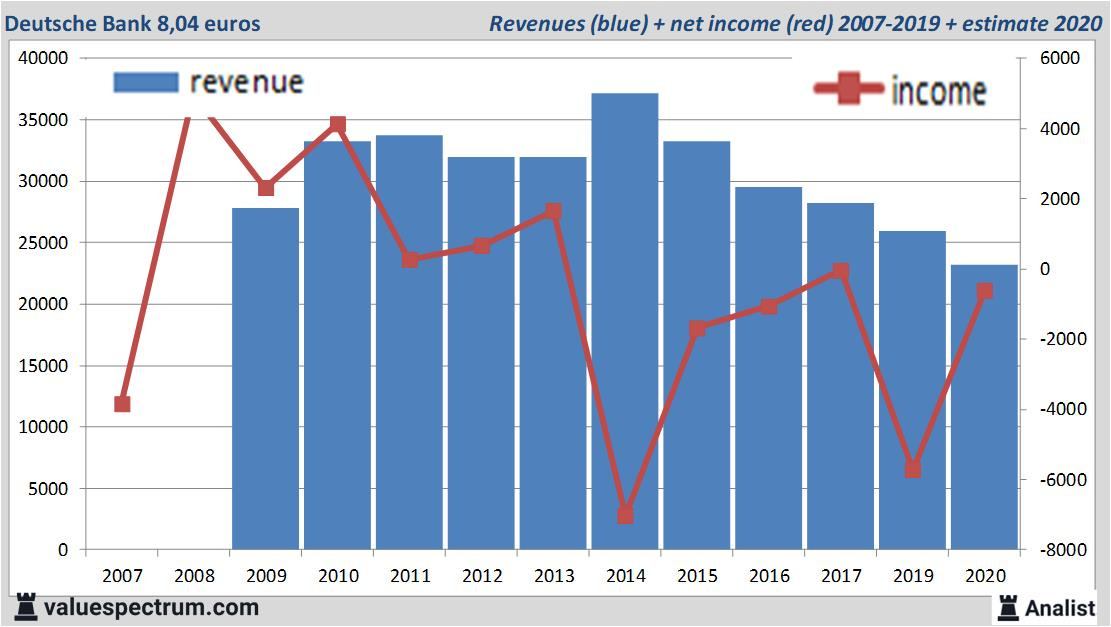
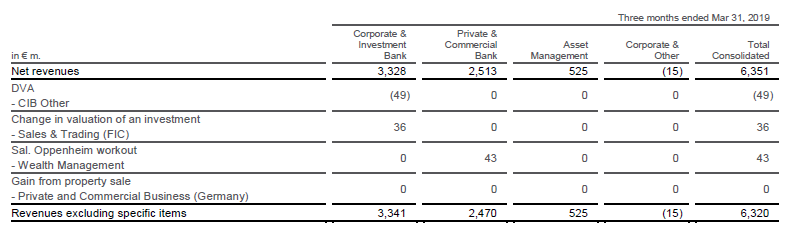
Revenue: Deutsche Bank generates billions in revenue annually, with investment banking and corporate banking as the key contributors. In 2022, Deutsche Bank reported revenues of approximately €27 billion.
Costs: Key costs include personnel expenses, technology investments, legal settlements, and regulatory compliance costs.
Profitability: Deutsche Bank has faced profitability challenges due to its legal and restructuring costs over the years, but it has shown signs of recovery, with improved profits in recent quarters, thanks to its restructuring initiatives.
Assets Under Management (AUM): The bank manages over €800 billion in assets through its wealth management and asset management divisions.
8. Marketing and Customer Acquisition
Target Market: Deutsche Bank serves a wide range of clients, including corporations, institutions, high-net-worth individuals, and retail customers, with a focus on investment banking, wealth management, and corporate banking services.
Marketing Channels:
Client Relationships: The bank leverages strong client relationships in corporate and investment banking, offering tailored solutions to large corporations and governments.
Digital Platforms: Deutsche Bank uses digital channels to promote its retail banking and wealth management services, emphasizing convenience and personalized solutions.
Sustainability Branding: As part of its sustainability strategy, Deutsche Bank markets its ESG-related products to socially conscious investors, emphasizing responsible and green investing.
Customer Engagement: Deutsche Bank engages clients through high-touch relationship management, advisory services, and thought leadership, offering insights on market trends and economic developments.
9. Challenges
Legal and Regulatory Issues: Deutsche Bank has faced numerous legal challenges, including fines for money laundering violations and involvement in financial scandals such as LIBOR manipulation. These have led to substantial financial penalties.
Profitability Pressures: The bank’s profitability has been impacted by restructuring costs, low-interest rates, and regulatory requirements, forcing it to adopt cost-cutting measures and streamline operations.
Intense Competition: Deutsche Bank faces strong competition from global and regional players in investment banking, asset management, and retail banking. In particular, the rise of fintech firms is challenging traditional banking models.
Digital Transformation: While Deutsche Bank has invested in digital banking and innovation, it faces challenges in integrating new technologies into its legacy systems, creating potential risks in efficiency and customer experience.
10. COVID-19 Impact
Market Volatility: The COVID-19 pandemic created significant market volatility, impacting Deutsche Bank’s investment banking operations. However, the bank benefited from increased trading revenues due to the surge in market activity.
Digital Acceleration: The pandemic accelerated Deutsche Bank’s digital transformation, with the bank enhancing its online banking platforms and remote advisory services to cater to customers during lockdowns.
Economic Uncertainty: The global economic slowdown and lower interest rates during the pandemic put pressure on the bank’s profitability, particularly in its lending and corporate banking divisions.
11. Future Prospects
Restructuring Plan: Deutsche Bank’s ongoing restructuring plan aims to focus on its core competencies in investment banking and wealth management, while exiting underperforming businesses such as retail banking in certain markets.
Sustainability Focus: As ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria become more important for investors, Deutsche Bank plans to expand its green finance offerings, positioning itself as a leader in sustainable banking.
Digital Banking: Deutsche Bank is investing heavily in fintech partnerships, blockchain technology, and AI-driven financial services to stay competitive in the rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Global Expansion: The bank is expected to strengthen its presence in high-growth markets such as Asia and the Middle East, capitalizing on increasing demand for corporate and investment banking services in these regions.
12. SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Strong brand recognition and global presence in investment banking.
A well-diversified portfolio of services, including corporate banking, wealth management, and asset management.
Extensive client relationships with corporations, governments, and institutions.
Weaknesses:
History of legal and regulatory issues, impacting profitability and reputation.
Challenges in digital transformation due to legacy systems and high operational costs.
Opportunities:
Growing demand for sustainable finance products, such as green bonds and ESG investments.
Expanding presence in emerging markets, particularly in Asia and the Middle East.
Opportunities in digital banking and fintech partnerships to enhance customer experience.
Threats:
Intense competition from global and regional financial institutions, as well as fintech disruptors.
Regulatory challenges and potential legal liabilities from past misconduct.
Macroeconomic uncertainty and potential impacts of future economic crises or geopolitical tensions.
13. Strategic Recommendations
Focus on Core Strengths: Deutsche Bank should continue focusing on its core businesses—investment banking, corporate banking, and wealth management—while divesting non-core assets and underperforming divisions.
Enhance Digital Transformation: Investing in AI, blockchain, and data analytics can help Deutsche Bank streamline its operations, reduce costs, and improve customer engagement.
Promote Sustainability: By positioning itself as a leader in sustainable finance, Deutsche Bank can attract ESG-conscious investors and expand its product portfolio to include more green financial products.
Strengthen Risk Management: Improving compliance and risk management practices can help Deutsche Bank avoid future legal challenges, protect its reputation, and ensure long-term sustainability.
14. Conclusion
Deutsche Bank has established itself as a global leader in financial services, particularly in investment banking and wealth management. However, it has faced significant challenges related to legal issues, regulatory pressures, and profitability. By continuing its restructuring efforts, investing in digital transformation, and promoting sustainability, Deutsche Bank is well-positioned for long-term growth and stability in the competitive global financial market.
HSB Important Articles and References :Share your feedback and tell us which case studies you'd like to see next by filling out this quick Google form! Click Here
Check and follow up:
1) WhatsApp Channel : Click Here
2) Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/homeschoolofbusiness.in/
Deutsche Bank (Wikipedia) : Click Here
Deutsche Bank Annual Report 2023 : Click Here
Quarterly Results : Click Here
The Case Study : Click Here
Apply for Jobs at Deutsche Bank : Click Here
The Website : Click Here
Services and Products by Deutsche Bank : Click Here
HSB Video Vault :-
What The Home School of Business Offers:
Business News Letters We Offer:
Business Case Study Series, Scam Series, Leadership Series, Industry Series, City Series, 5 Minute reads.Startup Tips Guide Series: Get step-by-step guidance from idea inception to IPO.
Your journey from an idea to IPO starts here!
Visit our website for all Posts: CLICK HERE
Best Regards,
The Home School of Business Team