Ola Cabs: A Comprehensive Business Case Study
1. Introduction
Ola Cabs, popularly known as Ola, is one of India’s largest ride-hailing platforms, offering a range of transportation services from cabs to auto-rickshaws. This case study provides an in-depth analysis of Ola's journey, business model, strategies, challenges, and future prospects.
2. Company Overview
Founders: Bhavish Aggarwal and Ankit Bhati
Founded: 2010
Headquarters: Bangalore, India
Industry: Transportation, Technology
Core Products: Ride-hailing services, Ola Auto, Ola Bike, Ola Electric, and Ola Foods
3. Market Analysis
Market Size: The Indian ride-hailing market was valued at approximately $3 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.6% from 2021 to 2026.
Consumer Behavior: Increasing urbanization, preference for convenience, and the affordability of ride-hailing services drive market growth.
Competitors: Uber, Meru Cabs, Rapido, and other local and regional transportation services.
4. Business Model
Ola operates on a multi-sided platform model, connecting riders with drivers through its app. The company has diversified its offerings to include various transportation modes and services.
Ride-Hailing: Connecting passengers with drivers for different vehicle options (Ola Mini, Ola Prime, Ola Lux, etc.).
Auto and Bike Services: Offering auto-rickshaw and bike ride-hailing services for last-mile connectivity.
Electric Vehicles: Launching Ola Electric to promote electric mobility solutions.
Food Delivery: Entering the food delivery market with Ola Foods.
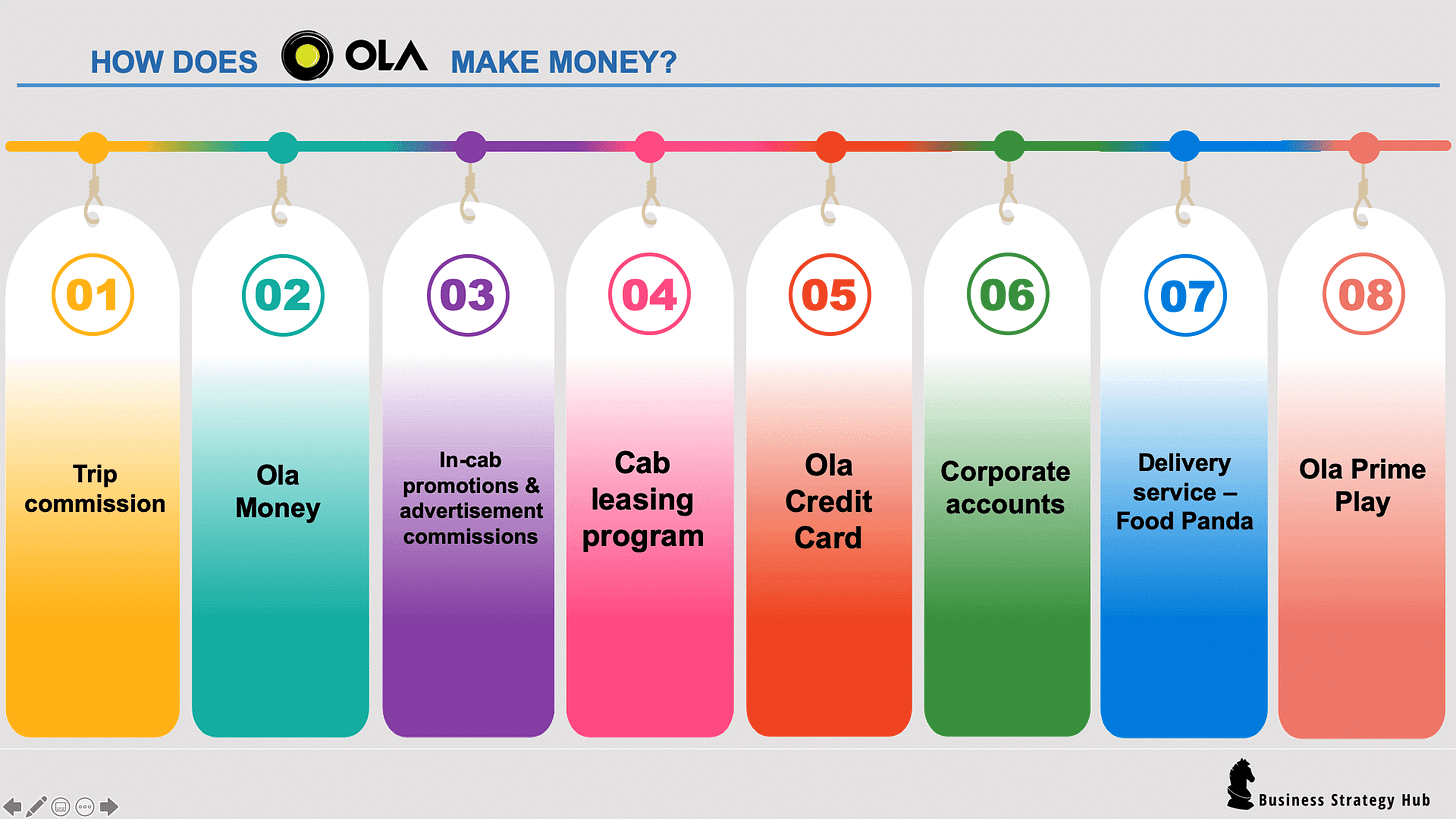
Revenue Streams: Commissions on ride fares, leasing fees from drivers, advertising, and subscription services (Ola Select).
5. Evolution and Growth
Initial Phase: Launched in Mumbai in 2010, quickly expanding to other major cities across India.
Geographical Expansion: Expanded operations to Australia, New Zealand, and the UK.
Product Diversification: Introduced various ride options, including auto-rickshaws, bikes, and luxury cars. Launched Ola Electric to tap into the EV market.
Funding: Raised significant capital from investors such as SoftBank, Tiger Global, and Sequoia Capital, reaching a valuation of over $6 billion.
6. Operational Strategy
Technology and Innovation: Continuous investment in technology for app development, route optimization, and customer experience.
Driver Partnerships: Recruiting and retaining drivers through incentives, flexible work hours, and support services.
Market Penetration: Aggressive market penetration strategies including subsidized fares, promotions, and strategic partnerships.
Regulatory Navigation: Engaging with local governments and regulatory bodies to ensure compliance and influence policy.
7. Financial Analysis
Revenue Streams: Major revenue sources include ride-hailing commissions, leasing fees, advertising, and subscription services.
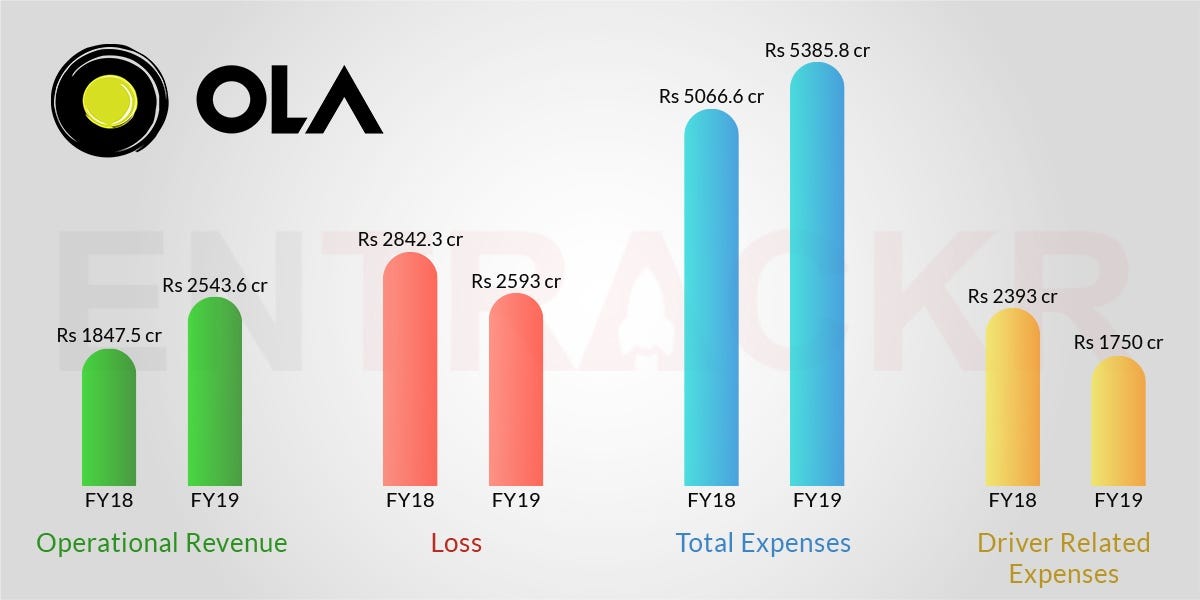
Cost Structure: Significant costs related to driver incentives, technology development, marketing, regulatory compliance, and legal expenses.
Profitability: Faced challenges in achieving profitability due to high operational costs and intense competition. However, improvements in operational efficiency and diversification efforts aim to achieve sustainable profitability.
8. Marketing and Customer Acquisition
Target Market: Urban consumers, young professionals, students, and businesses.
Marketing Channels: Digital marketing, social media campaigns, influencer partnerships, traditional advertising, and promotions.
Customer Engagement: Building a loyal customer base through personalized marketing, loyalty programs (Ola Select), and consistent service quality.
9. Challenges
Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex and varying regulations across different markets, including legal battles over driver classification.
Competition: Intense competition from other ride-hailing platforms and traditional taxi services.
Operational Efficiency: Managing high operational costs, ensuring driver retention, and maintaining service quality.
Public Perception: Addressing concerns related to safety, data privacy, and corporate governance.
10. COVID-19 Impact
The pandemic significantly impacted Ola’s ride-hailing business due to lockdowns and reduced travel. However, Ola adapted by enhancing its focus on safety protocols, introducing contactless payments, and expanding its delivery and electric vehicle services.
11. Future Prospects
Expansion into New Markets: Exploring opportunities in emerging markets and expanding existing services.
Technological Advancements: Continued investment in autonomous vehicles, electric vehicles, and AI to enhance service efficiency and sustainability.
Diversification: Expanding into new areas such as food delivery, healthcare transportation, and logistics.
Sustainability Initiatives: Commitment to promoting electric vehicles and implementing eco-friendly practices.
12. SWOT Analysis
Strengths: Strong brand recognition, extensive market presence, innovative technology, and diverse service offerings.
Weaknesses: High operational costs, regulatory challenges, and difficulties in achieving consistent profitability.
Opportunities: Growing demand for on-demand services, potential for new service offerings, and expansion into tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
Threats: Intense competition, regulatory changes, and economic downturns affecting consumer spending.
13. Strategic Recommendations
Optimize Operations: Invest in technology for better logistics management and cost optimization.
Expand Service Offerings: Diversify into related services like healthcare transportation and logistics to increase revenue streams.
Strengthen Regulatory Compliance: Develop robust compliance frameworks and engage proactively with regulatory bodies.
Enhance Customer Retention: Focus on personalized marketing, loyalty programs, and customer service to retain and engage customers.
Sustainability Focus: Promote sustainable practices, such as electric vehicle adoption and reducing the carbon footprint of operations.
14. Conclusion
Ola has revolutionized the transportation industry in India with its innovative business model and extensive market presence. Despite facing significant challenges, the company’s strong operational framework and strategic initiatives position it well for future growth. By focusing on operational efficiency, service diversification, and sustainability, Ola can continue to build on its strengths and achieve long-term success in the evolving mobility industry.
What The Home School of Business Offers:
Weekly Guest Seminars: Learn from industry student leaders and gain valuable insights.
Business News Letters We Offer:
Business Case Study Series, Scam Series, Leadership Series.Startup Tips Guide Series: Get step-by-step guidance from idea inception to IPO.
Your journey from an idea to IPO starts here!
Visit our website for all Posts: Home School of Business Website
Best Regards,
The Home School of Business Team
Download the Android App: Click Here
Download the iOS App: Click Here
Ola Cabs Website : Click Here
Business Case Study (Research Gate) : Click Here
Case Study (Medium) : Click Here
How Does Ola Cabs Earn Money? : Click Here