Spotify’s Global Music Takeover: Inside the Streaming Giant's Success and Challenges
Business Case Study Series
Spotify: A Comprehensive Business Case Study
1. Introduction
Spotify, a Swedish audio streaming and media services provider, has revolutionized the music industry by offering an extensive library of music, podcasts, and other audio content via a subscription-based model. Launched in 2008, it has grown to become the world’s largest music streaming platform, significantly shaping how people consume music. This case study explores Spotify's business model, growth strategies, challenges, and its adaptation to changing market dynamics, offering insights for Home School of Business students.
2. Company Overview
Founder: Daniel Ek and Martin Lorentzon
Founded: April 23, 2006
Headquarters: Stockholm, Sweden, and New York City, USA
Industry: Music Streaming and Media Services
Core Products: Music streaming, podcasts, exclusive artist content, and playlists
Global Presence: Available in 180+ markets, with over 500 million active users, including more than 220 million premium subscribers (as of 2024)
3. Market Analysis
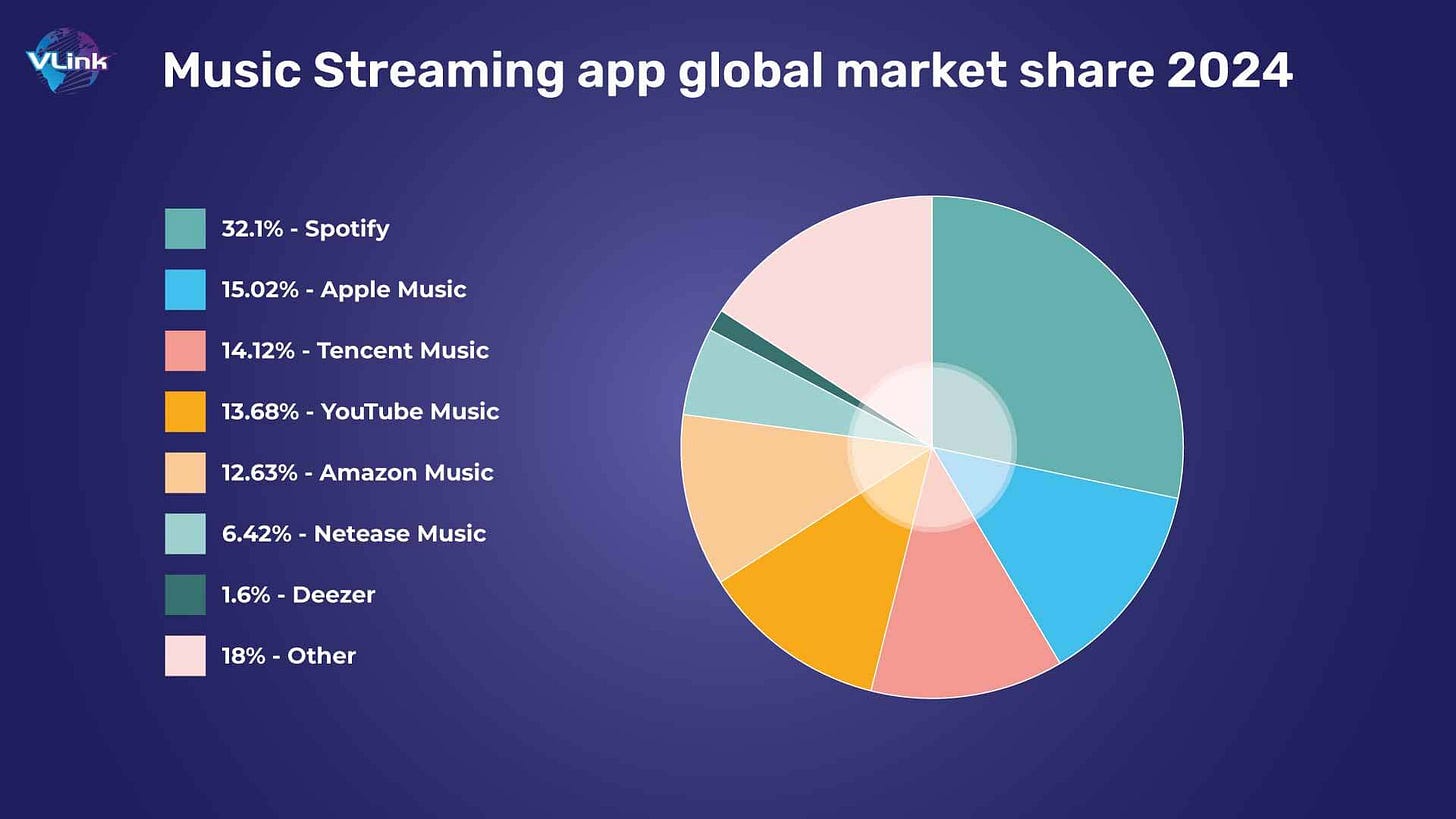
Market Size: The global music streaming market was valued at approximately $29.45 billion in 2021, with projections indicating it will grow to over $103 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 14.7%. Spotify holds the largest market share, competing against players like Apple Music, Amazon Music, and YouTube Music.
Consumer Behavior: The shift from physical and digital ownership of music to on-demand access through streaming services is driven by consumers’ desire for convenience, music discovery, and personalized experiences.
Key Competitors: Apple Music, Amazon Music, YouTube Music, Deezer, and Tidal.
4. Business Model
Spotify operates a "freemium" business model, offering both free, ad-supported access and premium, ad-free subscription options. The platform generates revenue from advertising on its free tier and subscription fees from its premium tier.
Product Range:
Free Tier: Users access music with advertisements and limited functionality (such as shuffle play on mobile devices).
Premium Tier: Ad-free listening, offline downloads, unlimited skips, higher audio quality, and more.
Podcasts: Spotify has invested heavily in podcasting, acquiring major podcast platforms and exclusive content rights (e.g., Joe Rogan Experience).
Spotify for Artists: Tools and analytics for musicians to understand their audience, promote their music, and track performance.
Revenue Streams:
Subscription Revenue: Premium subscriptions are the primary source of income, offering users enhanced features for a monthly fee.
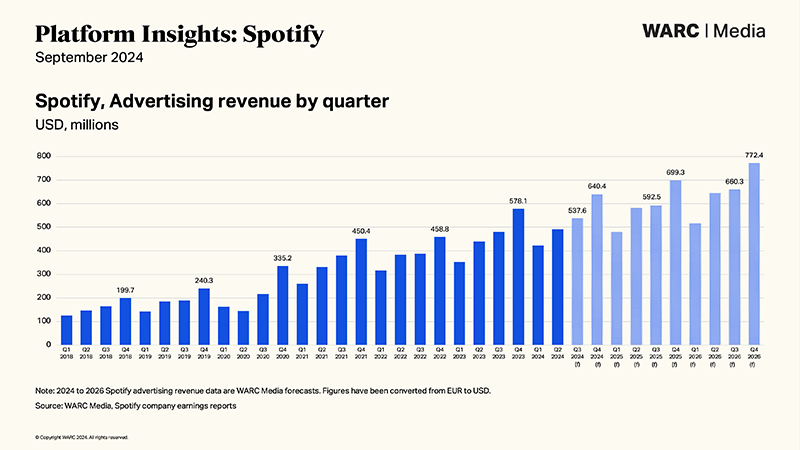
Advertising Revenue: Ads played on the free tier and within podcasts contribute a substantial portion of Spotify’s total revenue.
Partnerships: Deals with mobile carriers, brands, and hardware providers to bundle Spotify services or offer them at discounted rates to drive adoption.
5. Evolution and Growth
Early Beginnings: Founded in 2006, Spotify officially launched its music streaming platform in 2008 as a solution to the increasing problem of music piracy. With a mission to provide easy and legal access to music, Spotify initially offered a free, ad-supported service and quickly gained traction.
Expansion: Spotify expanded globally by strategically entering new markets and partnering with record labels and rights holders. Its continuous focus on user experience and music discovery, via personalized playlists like Discover Weekly, fueled growth.
Investment in Podcasts: Spotify diversified its content offering by acquiring Gimlet Media, Anchor, and Parcast in 2019 and securing exclusive rights to The Joe Rogan Experience in 2020. This strategic pivot positioned Spotify as a major player in the podcasting world.
6. Operational Strategy
Freemium Model: Spotify’s freemium model allows users to experience the service at no cost with advertisements, enticing them to upgrade to the premium tier for additional features like offline listening and no ads.
Data-Driven Personalization: Leveraging AI and machine learning, Spotify provides personalized playlists (e.g., Discover Weekly, Daily Mix), making music discovery an integral part of the user experience and increasing user retention.
Partnerships and Collaborations: Spotify partners with telecommunications companies, device manufacturers, and car brands to pre-install its app, bundle premium subscriptions, or offer extended free trials. These partnerships help expand its reach and user base.
Content Investment: Spotify has focused on acquiring and producing original podcast content to diversify its offerings and boost engagement. With over 5 million podcasts available on its platform, Spotify aims to dominate the podcasting space.
Sustainability: Spotify has committed to reaching net-zero carbon emissions by 2030, aligning its business operations with environmental sustainability goals, including sustainable streaming and carbon offset projects.
7. Financial Analysis
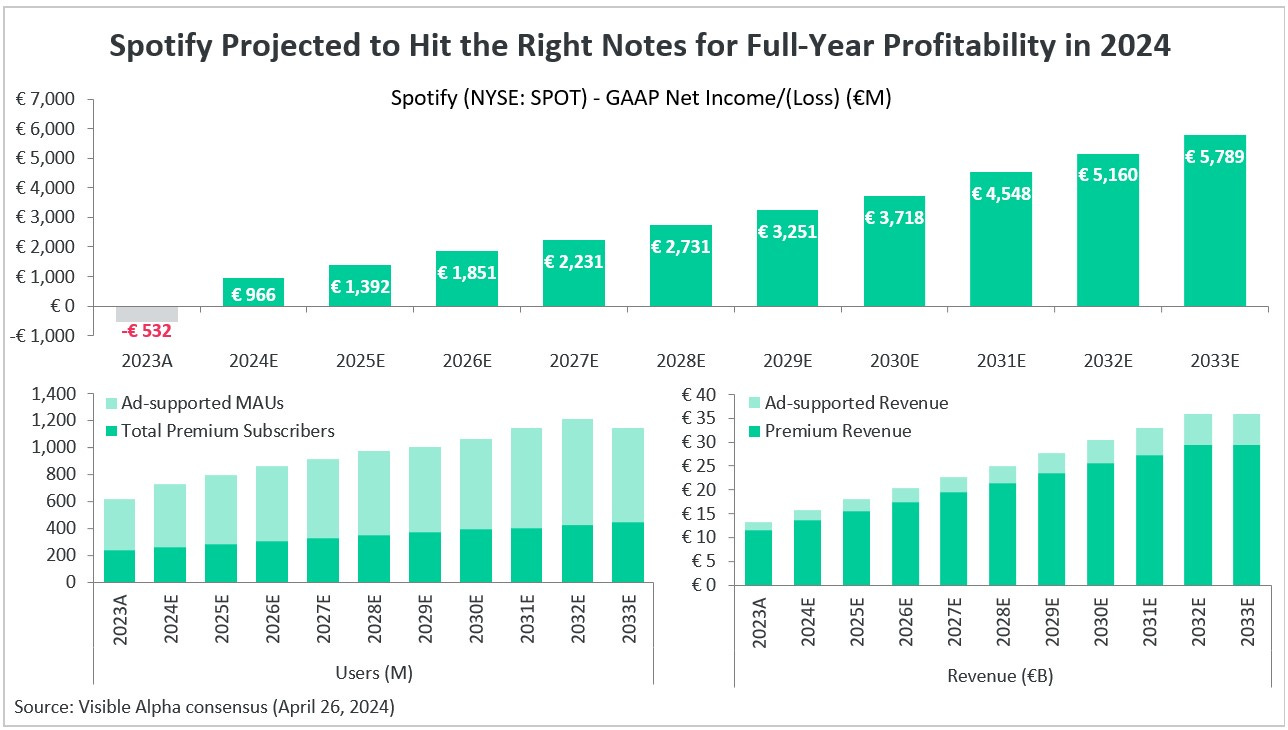
Revenue: In 2023, Spotify generated around €12.8 billion in revenue, with subscription fees making up approximately 85% of the total, while advertising accounted for the remaining 15%.
Costs: Spotify’s main expenses include content licensing fees to music rights holders, artist royalties, platform development, marketing, and podcast production costs. Artist and label payments are the most significant cost driver.
Profitability: While Spotify has achieved impressive revenue growth, it continues to operate at a net loss, driven by high content licensing costs and investments in podcasting and platform innovation. Spotify’s focus on user growth and market share means profitability remains a long-term goal.
8. Marketing and Customer Acquisition
Target Market: Spotify’s target market includes a wide demographic, from casual listeners to audiophiles, with its freemium model allowing it to cater to users in different income brackets. Its premium offering targets users who prioritize ad-free listening and offline access.
Marketing Channels:
Digital Advertising: Spotify employs social media, search engine marketing, and digital ads to attract both free and premium subscribers.
Content Partnerships: Spotify collaborates with brands and influencers to create unique, sponsored playlists and co-branded campaigns.
Telecom Bundles: Partnerships with telecom providers offering bundled services or discounted premium subscriptions have proven effective in driving user acquisition.
Customer Engagement: Spotify prioritizes personalized engagement with features like Discover Weekly, Release Radar, and Wrapped, an annual recap of a user’s listening habits that goes viral on social media. These personalized features keep users engaged and increase retention.
9. Challenges
Profitability Issues: Despite generating significant revenue, Spotify continues to report net losses due to high royalty fees paid to record labels and artists. Achieving long-term profitability remains a major challenge for the company.
Licensing Costs: Spotify pays the majority of its revenue to rights holders, including record labels, songwriters, and publishers. Negotiating more favorable licensing deals remains a challenge as the company aims to improve margins.
Competition: Spotify faces fierce competition from Apple Music, Amazon Music, YouTube Music, and other streaming platforms, many of which have deeper pockets or are part of larger ecosystems (e.g., Apple’s hardware-driven services).
Artist Royalty Disputes: Spotify has faced criticism from artists and rights holders over low per-stream payouts. As the company grows, it must balance the demands of artists with its need to remain profitable.
10. COVID-19 Impact
Increased Consumption: The pandemic led to a surge in digital media consumption, including music and podcasts, as people spent more time at home. Spotify saw an increase in both free and premium users.
Podcast Boom: During the pandemic, podcast consumption skyrocketed, benefiting Spotify’s strategy to expand into podcasting. With more people seeking diverse audio content, podcasts became an essential part of Spotify’s growth strategy.
Advertising Impact: While user numbers grew, Spotify experienced some short-term declines in advertising revenue during the early stages of the pandemic due to budget cuts by advertisers.
11. Future Prospects
Growth in Emerging Markets: Spotify is expected to focus on expanding its user base in emerging markets such as India, Brazil, and Southeast Asia, where streaming is becoming more popular, but competition is also intense.
Monetization of Podcasts: Spotify’s foray into podcasts presents new monetization opportunities, including exclusive content deals, ad placements, and paid subscription models for premium podcast content.
Improving Artist Relations: Spotify will need to continue working on improving its relationship with artists, offering better tools for promotion, data insights, and potentially better royalties to retain artist trust and content on the platform.
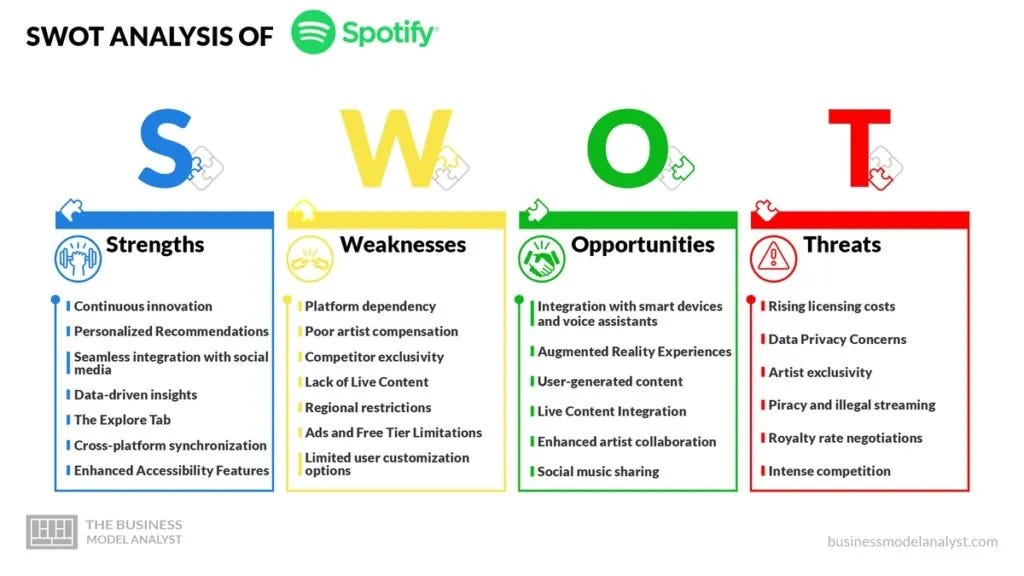
12. SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Leading global market share in music streaming.
Strong brand recognition and user loyalty.
Extensive library of music and podcasts.
Personalized music discovery tools.
Weaknesses:
High dependency on content licensing agreements and artist royalties.
Ongoing profitability challenges.
Intense competition from rivals with deeper ecosystems.
Opportunities:
Expansion into emerging markets.
Increased investment in exclusive content and podcasting.
Development of new revenue streams through partnerships and advertising innovations.
Threats:
Rising competition from Apple Music, YouTube Music, and others.
Legal and regulatory challenges related to licensing and royalty payments.
Market saturation in developed regions.
13. Strategic Recommendations
Expand Content Offerings: Spotify should continue investing in original and exclusive content, particularly in podcasting, to differentiate itself from competitors and create new revenue opportunities.
Focus on Emerging Markets: Tailoring services to local markets and partnering with telecom providers in high-growth regions such as India, Latin America, and Southeast Asia can help drive user acquisition.
Artist Support and Royalties: Improving artist royalties and support tools could enhance Spotify’s reputation within the artist community and potentially attract exclusive content.
Monetize Podcasts: Spotify should continue exploring ways to monetize its podcast content through premium subscriptions, ads, and exclusive shows.
14. Conclusion
Spotify has established itself as the world’s leading music streaming service by offering a vast music library, personalized recommendations, and a freemium model that attracts a broad user base. However, challenges such as high content licensing costs, intense competition, and the path to profitability remain. By expanding into new markets, growing its podcasting business, and improving artist relations, Spotify is well-positioned to continue leading the music streaming industry in the future.
HSB Important Articles and References :Share your feedback and tell us which case studies you'd like to see next by filling out this quick Google form! Click Here
Check and follow up:
1) WhatsApp Channel : Click Here
2) Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/homeschoolofbusiness.in/
Spotify (Wikipedia) : Click Here
Spotify Premium : Click Here
The Business Model : Click Here
The Marketing Strategy : Click Here
Spotify Financials : Click Here
Should you buy the Spotify Stock : Click Here
HSB Video Vault :-
What The Home School of Business Offers:
Business News Letters We Offer:
Business Case Study Series, Scam Series, Leadership Series, Industry Series, City Series, 5 Minute reads.Startup Tips Guide Series: Get step-by-step guidance from idea inception to IPO.
Your journey from an idea to IPO starts here!
Visit our website for all Posts: CLICK HERE
Best Regards,
The Home School of Business Team